
This means that the ICE table for the dissociation of the silver sulfate will look like this #"AgNO"_ (3(aq)) -> "Ag"_ ((aq))^(+) + "NO" _(3(aq))^(-)#Īs shown by the #1:1# mole ratios that exist between the solid and the dissolved ions, a #"0.10 M"# silver nitrate solution will have Unlike silver sulfate, silver nitrate is soluble in aqueous solution, which means that it dissociates completely to form silver cations and nitrate anions

This time, you're interested in finding the molar solubility of silver sulfate in a solution that is #"0.10 M"# silver nitrate, #"AgNO"_3#. This means that in a saturated solution of silver sulfate, the concentration of the salt that will dissolve to produce ions is equal to Rearrange to solve for #s#, the molar solubility of silver sulfate in pure water #color(purple)("E")color(white)(aaaaaacolor(black)(-)aaaaaaaaaaaaacolor(black)(color(blue)(2)s)aaaaaaaaaaacolor(black)(s)#īy definition, the solubility product constant, #K_(sp)#, is equal to #color(purple)("C")color(white)(aaaaaacolor(black)(-)aaaaaaaaaaacolor(black)((+color(blue)(2)s))aaaaaaacolor(black)((+s))# #color(purple)("I")color(white)(aaaaaacolor(black)(-)aaaaaaaaaaaaaacolor(black)(0)aaaaaaaaaaacolor(black)(0)# You can use an ICE table to find the equilibrium concentration of the two ions
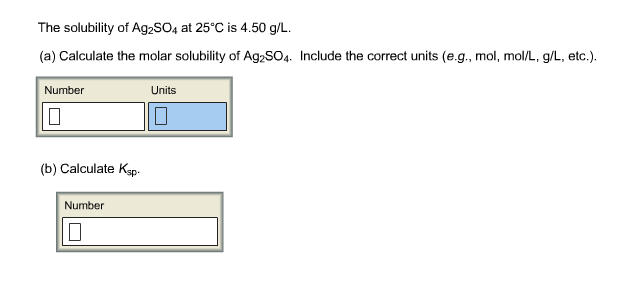
Now, when you dissolve the salt in pure water, the initial concentration of the dissolved ions will be equal to zero. Silver sulfate, #"Ag"_2"SO"_4#, is considered insoluble in aqueous solution, which implies that a dissociation equilibrium between the dissociated ions and the undissolved solid is established when you dissolve the salt in water.
#Ag 2so 4 how to
I'll show you how to solve parts (a) and (b) and leave part (c) to you as practice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
